In this comprehensive guide, we’ll go through the various tips and approaches on how to pay off student loans fast to help you become debt-free faster.
In today’s world, higher education often comes with the big price tag of student loans. The burden of student debt can be overwhelming, but fear not, as there are effective strategies to pay off student loans early and quickly. Whether you’re wondering how to repay student loans efficiently, looking for ways of how to pay off private student loans, or seeking the best way to pay student loans, you’ll find answers here.
Key Takeaways
-
- Start by gathering all the details about your student loans, including types, interest rates, and grace periods. Knowing your loans is the first step to managing them effectively.
- Understand the differences between Federal and Private student loans and how they impact your repayment options.
- Comprehend how interest accrues and the importance of minimizing it.
- Selecting the right plan based on your financial situation is crucial. Consider options like Income-Driven Plans for flexibility.
- The Avalanche Method involves paying off high-interest loans first. This strategy can save you money over time by reducing interest payments.
- Tailor your repayment strategy to fit your financial circumstances. Seek professional guidance if you face financial hardship.
How to Pay Off Student Loans Fast: Step-by-Step
It all begins with knowledge, strategy, and determination. Here, we will see a roadmap to help you navigate the complexities of student loan repayment, providing you with the insights needed to accelerate your journey towards becoming debt-free.
Understanding Your Student Loans
Before going into the repayment strategies, it’s
essential to understand your student loans fully. Start by gathering all the
necessary details about your loans, including the lender’s information,
interest rates, outstanding balances, and loan types.
Understanding this is
the first step towards successfully managing and paying off student loans. By
gathering loan details, differentiating between loan types, and grasping
interest rates, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of student
debt. With the right knowledge and a solid plan, you can able to pay back
student loans and take control of your financial future.
Gathering Loan Details
You need to know your adversary before you can conquer your student loans. Gathering loan details is your first step toward financial clarity. This includes:
Lender’s Information
Identify the entity holding your student loans, whether a federal agency or a private institution. Different lenders may offer varying repayment options.
Outstanding Balances
Determine the exact amount you owe for each loan. This information will be crucial when crafting your repayment plan.
Differentiating Between Loan Types
Understanding the types of loans you have is essential, as each comes with its own set of rules and repayment options.
Federal Student Loans: Federal loans are backed by the U.S. government and offer benefits like income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs. Example: Stafford loans, PLUS loans, and Perkins loans are all federal student loans.
Private Student Loans: Private loans are provided by banks, credit unions, or other private lenders. They typically have fewer borrower protections but can offer competitive interest rates. Example: A private loan from a bank like Citibank or a credit union like Navy Federal Credit Union.
Grasping Interest Rates
Interest rates play a significant role in how much you’ll ultimately repay on your student loans.
- Fixed Interest Rates: Fixed interest rates remain constant throughout the life of the loan. This means your monthly payments are predictable. Example: If you have a fixed interest rate of 4.5% on a $20,000 loan, your monthly payment will always be the same.
- Variable Interest Rates: Variable interest rates can fluctuate over time, which can impact your monthly payments. Example: Your variable interest rate might start at 3.5% but increase to 5.0% in the future.
- Subsidized vs. Unsubsidized: Federal loans can be subsidized or unsubsidized. Subsidized loans don’t accrue interest while you’re in school or during deferment, making them a more affordable option. Example: A subsidized Stafford loan with an interest rate of 3.0% won’t accumulate interest during your college years.
Choosing the Right Repayment Plan
Choosing the right repayment plan is a critical step toward managing your student loan debt effectively. Whenever you are looking forward for a higher education with keeping in mind the student loans, one question that always come up in your mind that how do I pay off my student loans.
When it comes to paying back student loans, one size doesn’t fit all. Choosing the right repayment plan is crucial to managing your student loan debt effectively. With various options available, you can tailor your repayment strategy to your financial situation and goals.
1. Federal Repayment Plans
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan is the default option for federal student loans. It offers fixed monthly payments over a 10-year term. Example: If you have a $30,000 loan with a 5% interest rate, your monthly payment would be approximately $318.
Graduated Repayment Plan
The Graduated Repayment Plan starts with lower monthly payments that increase every two years. It’s suitable for borrowers expecting their income to rise. Example: You start with a $200 monthly payment, which increases to $400 over time.
Extended Repayment Plan
The Extended Repayment Plan extends the repayment term to 25 years, lowering your monthly payments. It’s ideal for borrowers with high loan balances. Example: A $50,000 loan with a 6% interest rate would result in a monthly payment of approximately $288.
2. Income-Driven Plans
Income-Based Repayment (IBR)
IBR caps your monthly payments at a percentage of your discretionary income, making it manageable for borrowers with low earnings. Example: If your discretionary income is $20,000 and you’re required to pay 10%, your monthly payment would be $167.
Pay As You Earn (PAYE)
PAYE is similar to IBR but with lower monthly payments. It’s available to borrowers with a demonstrated financial hardship. Example: With a discretionary income of $20,000 and a 10% payment requirement, your monthly payment would be $138.
Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE)
REPAYE extends income-driven benefits to more borrowers and offers affordable payments. Example: With the same discretionary income and 10% payment requirement, your monthly payment would remain at $138.
3. Customizing to Your Financial Situation
Assessing Your Finances
To choose the right repayment plan, assess your financial situation, including your income, expenses, and future expectations. Example: Consider your monthly income, rent or mortgage payments, groceries, and other expenses.
Loan Forgiveness
Some income-driven plans offer loan forgiveness after a certain number of qualifying payments. Evaluate if this aligns with your long-term financial goals. Example: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) offers forgiveness after 120 qualifying payments for eligible public service workers.
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you’re uncertain about the best repayment plan, consult with a financial advisor or loan counselor. They can provide personalized recommendations. Example: A financial advisor can help you analyze your unique financial circumstances and goals.
Crafting a Strategic Budget
The first step in crafting a budget is defining your financial goals. Determine how much you want to allocate towards paying off your student loans each month.
To pay off student loans quickly, you need a well-structured budget. Create a monthly budget that outlines your income sources and all expenses. Allocate a significant portion of your budget to loan payments, with the aim of exceeding the minimum required payments whenever possible.
You need to know your financial landscape. Track your monthly income and expenses to understand your cash flow.
Review your expenses to identify areas where you can cut back and allocate more funds towards loan repayment.
1. Create a Comprehensive Budget
1.1 Fixed vs. Variable Expenses
Categorize your expenses into fixed (constant) and variable (fluctuating) categories. This will help you prioritize your spending. Example: Fixed expenses include rent and utilities, while variable expenses include dining out and entertainment.
1.2 Emergency Fund
A crucial part of your budget is setting aside money for emergencies. Having an emergency fund ensures you won’t have to rely on credit cards if unexpected expenses arise.
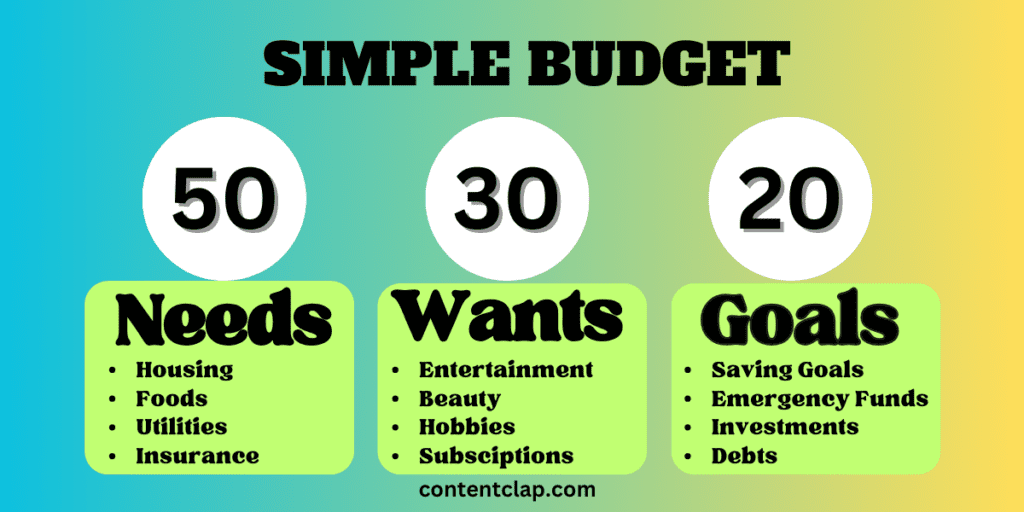
1.3 The 50/30/20 Rule
One popular budgeting approach is the 50/30/20 rule, where 50% of your income covers needs, 30% goes to wants, and 20% is allocated for savings and debt repayment. Example: If you earn $3,000 per month, $1,500 would go to needs, $900 to wants, and $600 for savings and debt repayment.
2. Allocating for Loan Payments
2.1 Prioritizing Loan Payments
Make your student loan payments a priority in your budget. Allocate a specific portion of your monthly income towards paying off your loans. Example: If your minimum loan payment is $300, aim to allocate an additional $200 from your budget towards loan repayment.
2.2 Staying Consistent
Consistency is key to successful loan repayment. Make sure to stick to your budget and continue making payments on time. Example: Set up automatic payments to ensure you never miss a due date.
Tackling High-Interest Loans First
Tackling high-interest student loans using the Avalanche Method is a smart financial move. It allows you to reduce interest payments, save money in the long run, and become debt-free sooner.
Concentrate your efforts on paying off loans with the highest interest rates first. This strategy, known as the “avalanche method,” minimizes the total interest paid over time, propelling you toward debt freedom.
The Avalanche Method is a debt repayment strategy that focuses on tackling high-interest loans before other debts. The concept is straightforward: you prioritize loans with the highest interest rates, making larger payments towards them while paying the minimum on lower-interest loans. Once the high-interest loans are paid off, you redirect the funds to the next high-interest loan until all your debts are cleared.
The steps are as follows:
- The first step in implementing the Avalanche Method is to gather all the necessary details about your student loans.
- Differentiate between federal and private loans, as they may have distinct repayment options and benefits.
- Interest rates play a pivotal role in the Avalanche Method. The higher the interest rate, the more your debt grows if left unpaid.
- To successfully implement the Avalanche Method, you need a well-structured budget.
- Allocate as much as possible towards your high-interest loans while paying the minimum on lower-interest loans.
- Stay committed to your budget and repayment plan.
Reducing Interest Payments: An Example
Let’s illustrate the effectiveness of the Avalanche Method with an example. Suppose you have two student loans:
Loan A: $10,000 with an interest rate of 6%
Loan B: $8,000 with an interest rate of 8%
Using the Avalanche Method, you prioritize Loan B due to its higher interest rate. By allocating extra funds towards Loan B while making minimum payments on Loan A, you’ll pay off Loan B faster. This not only reduces your overall debt but also minimizes the total interest you pay.
Exploring Loan Forgiveness Programs
Student loans can be a significant financial burden, but there are options available to ease this burden. One such option is loan forgiveness programs. Here, we will discuss about two prominent forgiveness programs: Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) and Teacher Loan Forgiveness.
Depending on your career path and loan types, you may be eligible for loan forgiveness programs. Notable examples include Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) and Teacher Loan Forgiveness, which offer partial or complete forgiveness after a specified number of qualifying payments or years of service. Investigate these options to see if they apply to your situation.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is a federal program designed to forgive the remaining student loan balance for borrowers who work in qualifying public service jobs. This program is an excellent option for those who have a passion for public service and are willing to commit to it.
- To be eligible for PSLF, you must work full-time for a qualifying employer, such as a government or nonprofit organization.
- Your job must also fall under specific categories, including public health, education, and law enforcement.
- Not all student loans are eligible for PSLF. To qualify, you must have federal Direct Loans.
- To benefit from PSLF, you should be on an income-driven repayment plan.
Teacher Loan Forgiveness
Teacher Loan Forgiveness is specifically designed for educators who work in low-income schools or educational service agencies. This program provides loan forgiveness for teachers who have made a significant commitment to the field of education.
- To be eligible for Teacher Loan Forgiveness, you must teach full-time for five consecutive years in a low-income school or educational service agency.
- Your teaching service must be in a subject area that corresponds to your teaching certification.
- Under this program, you can receive up to $17,500 in loan forgiveness, depending on your subject area and level of teaching.
- Highly qualified math and science teachers can qualify for the maximum amount.
Harnessing the Power of Extra Payments
Harnessing the power of extra payments is a smart strategy for expediting your journey to becoming debt-free. By understanding the concept of extra payments, instructing lenders to apply them to your loan’s principal, and incorporating them into your financial plan, you can take control of your student loan debt and achieve financial freedom sooner than you might have imagined.
- Every extra payment you make directly reduces your principal balance, leading to less interest paid over the life of the loan. Consider making bi-weekly or additional payments whenever feasible. Ensure you instruct your lender to apply these payments to the principal, not the interest.
- Extra payments, also known as additional payments or prepayments, are payments made above and beyond your regular monthly student loan payment.
- These payments are entirely voluntary and can be made at any time throughout the year.
- The primary purpose of making extra payments is to accelerate the reduction of your student loan debt.
Seeking Employment Benefits
Explore job opportunities that offer student loan
repayment assistance as part of their benefits package. Some employers provide
financial aid to help their employees pay off student loans faster.
Incorporating loan assistance into your job search criteria can be a smart
move.
Employer Assistance Programs?
Employer Assistance Programs are benefits offered by
companies to help their employees manage and pay off their student loans. These
programs can vary widely in scope and eligibility criteria.
Types of Assistance Programs
There are several types of employer assistance programs, including:
Loan Repayment Assistance Programs (LRAPs): These programs provide direct financial assistance to help employees pay off their student loans. Employers may contribute a fixed amount or match employee contributions.
Tuition Reimbursement Programs: While primarily designed for ongoing education, some employers allow employees to use tuition reimbursement for student loan payments.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Public service employers, such as government agencies and nonprofit organizations, may qualify employees for PSLF, leading to loan forgiveness after a set number of payments.
Employer Student Loan Contributions: Some employers offer a monthly contribution toward an employee’s student loan payment, effectively reducing the overall debt burden.
Incorporating Loan Assistance into Your Job Search
When conducting your job search, take the time to research prospective employers. Look for companies that offer student loan assistance as part of their benefits package. You can often find this information on the company’s website or by contacting their HR department.
Don’t be afraid to ask about student loan assistance benefits during job interviews. It’s a valid question, and employers appreciate candidates who show interest in their benefits package.
Consider the entire benefits package when assessing a job offer. While student loan assistance is valuable, it’s essential to evaluate other benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and career growth opportunities.
Conclusion
You’ve reached the end of our comprehensive guide on how to pay off student loans fast. We’ve explored numerous strategies, tips, and repayment plans that can help you tackle your student loan debt head-on and pave the way toward financial freedom.
In this journey, you’ve learned the importance of:
Budgeting: Crafting a strategic budget that allocates funds specifically for loan payments.
Choosing the Right Repayment Plan: Selecting the repayment plan that aligns with your financial situation and future goals.
Tackling High-Interest Loans First: Implementing the Avalanche Method to reduce interest payments effectively.
Harnessing the Power of Extra Payments: Accelerating debt reduction by making additional contributions.
Exploring Loan Forgiveness Programs: Investigating options like Public Service Loan Forgiveness and Teacher Loan Forgiveness.
Seeking Employment Benefits: Leveraging employer assistance programs to ease your loan burden.
By following these strategies and considering your unique circumstances, you can take control of your student loan debt and repay it efficiently. Remember that paying off your loans fast requires dedication, discipline, and a clear plan. Stay focused on your financial goals, and with time and effort, you’ll achieve the freedom you deserve.
FAQs
Is it possible to pay off student loans faster than the standard repayment plan suggests?
Yes, by following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can expedite your loan repayment significantly.
What is the best repayment plan for me if I have a variable income?
Consider an Income-Driven Repayment Plan, such as Income-Based Repayment (IBR) or Pay As You Earn (PAYE), which adjusts your payments based on your income.
How can I find out if I qualify for loan forgiveness programs?
Review the specific eligibility criteria for programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness or Teacher Loan Forgiveness and monitor your progress carefully.
What if I face unexpected financial challenges during repayment?
Contact your loan servicer to explore options like deferment, forbearance, or income-driven repayment adjustments.
Should I refinance my student loans?
Refinancing can be beneficial if you have high-interest loans and strong credit. However, be cautious when refinancing federal loans, as you may lose valuable federal benefits.





